Hong Kong’s Food and Environmental Hygiene Department (FEHD) is taking proactive steps to combat the spread of Chikungunya fever through targeted mosquito control measures. In a recent radio program, Senior Superintendent Hung Sai-kit outlined a comprehensive strategy designed to quickly respond to and mitigate potential disease transmission.
When a Chikungunya fever case is confirmed, the FEHD will launch an immediate and thorough intervention. Within just 24 hours of diagnosis, authorities will conduct vector investigations at the patient’s residence, applying insecticides and removing any stagnant water that could serve as mosquito breeding grounds. The control efforts will extend beyond the immediate home, covering a 250-meter radius that includes other locations the patient may have visited during their infectious period.
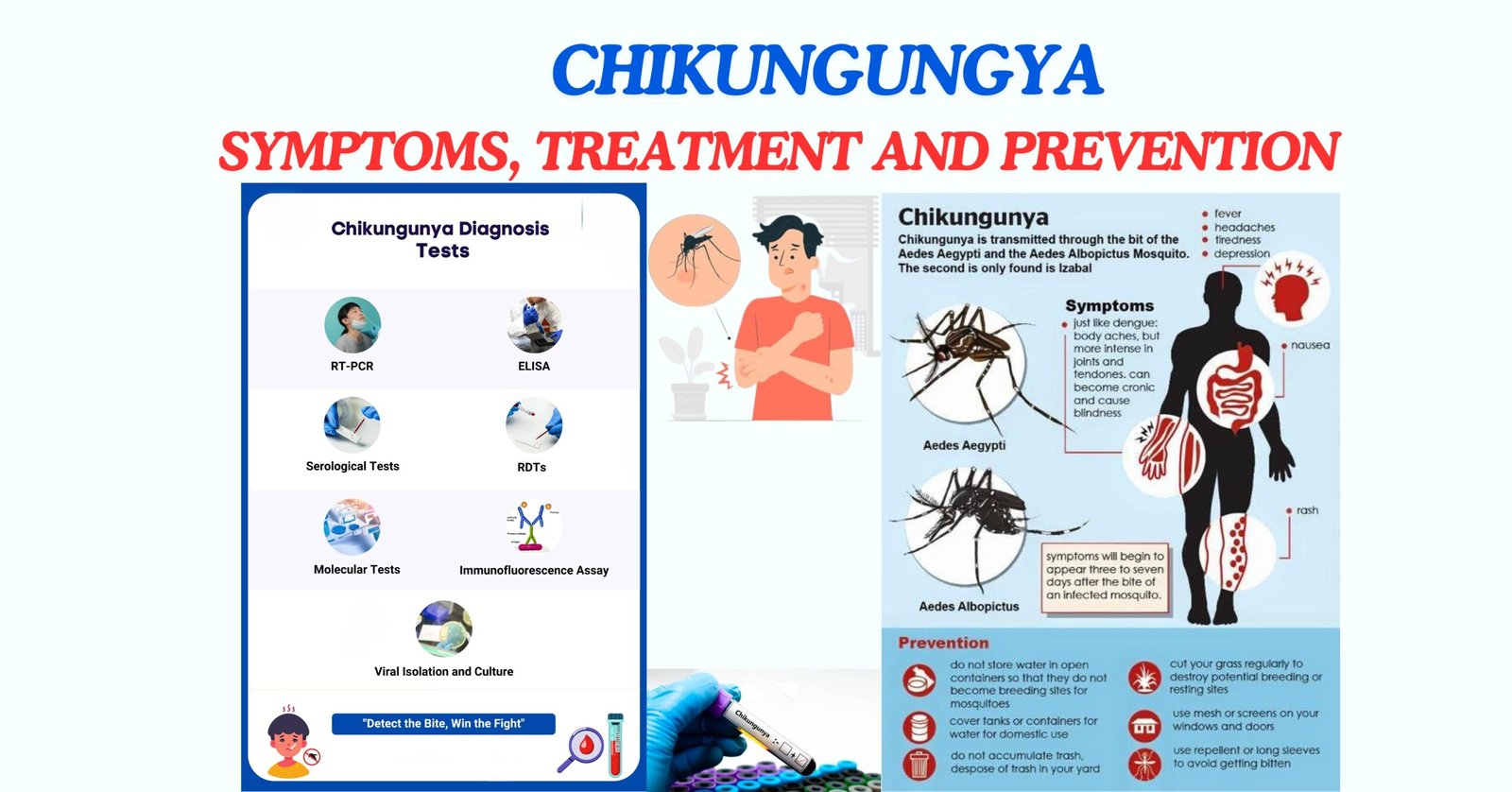
The current surveillance data provides some reassurance. According to Hung, the Gravidtrap Index for Aedes albopictus—the mosquito species responsible for transmitting Chikungunya—is currently below 10 percent across 58 monitored areas. This low index suggests that existing prevention measures are effectively keeping mosquito populations in check. However, the FEHD remains vigilant, prepared to take immediate action if the index shows any signs of increase.
Public health education is a crucial component of the department’s strategy. By raising community awareness about mosquito control, the FEHD aims to empower residents to participate actively in preventing disease spread. This approach recognizes that effective disease management requires collaboration between government authorities and the public.
The upcoming National Games have prompted additional preventive measures. FEHD will intensify inspections at event venues, working closely with operators to eliminate potential mosquito breeding sites. Venue managers will receive guidance on strengthening mosquito prevention protocols, ensuring public safety during these important sporting events.
Chikungunya fever is a viral disease transmitted primarily through mosquito bites, making vector control critical in preventing its spread. The symptoms can be debilitating, including fever, joint pain, and muscle aches, which can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. By implementing these swift and comprehensive measures, Hong Kong demonstrates a proactive approach to public health management.
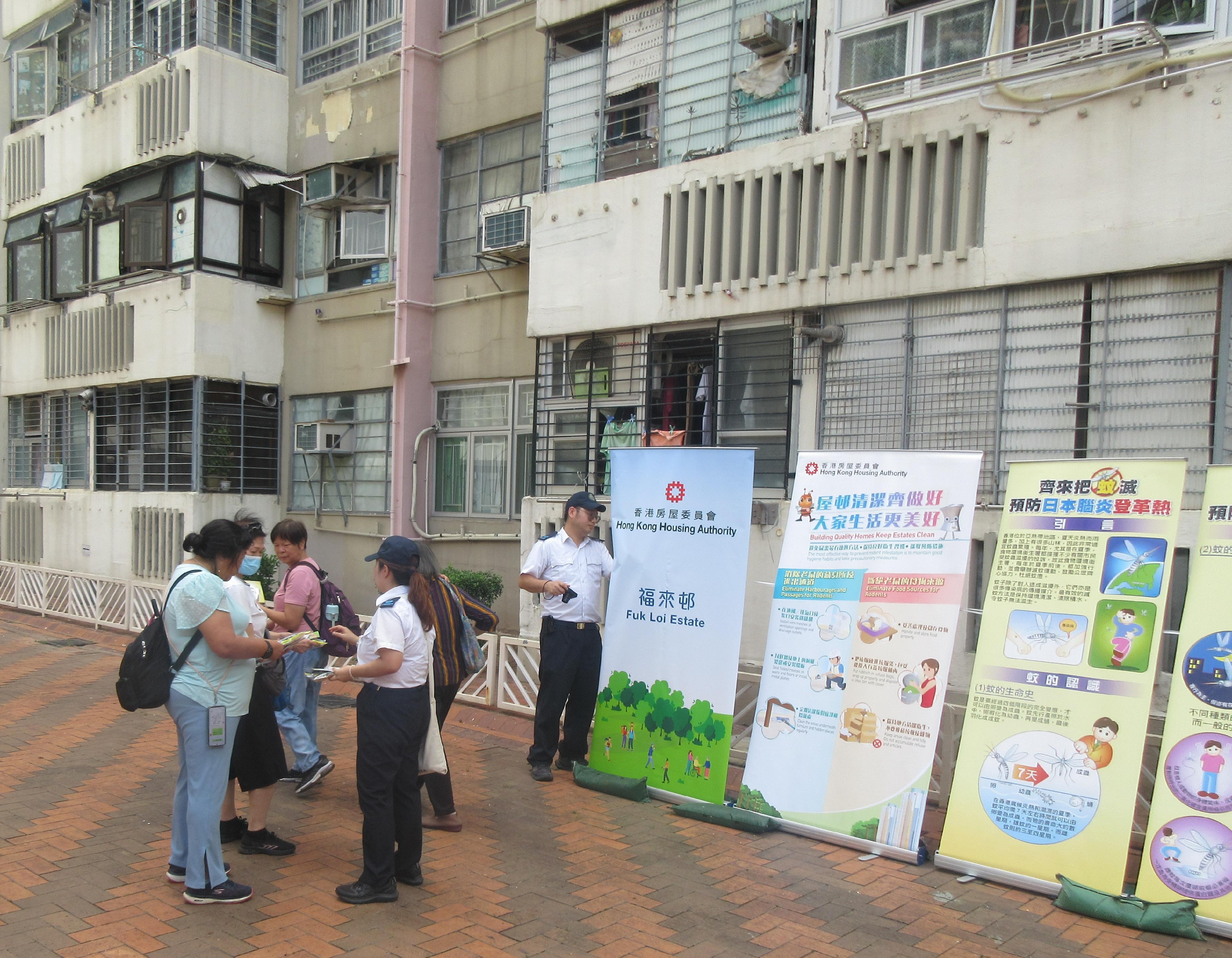

The FEHD’s strategy represents a multi-layered approach to disease prevention. Rapid response, targeted interventions, continuous monitoring, and public education work together to create a robust defense against potential outbreaks. This comprehensive plan not only addresses immediate risks but also builds long-term resilience in the community’s health infrastructure.
As cities worldwide grapple with emerging infectious diseases, Hong Kong’s methodical and science-driven approach offers a model for effective public health management. By combining technological surveillance, quick intervention, and community engagement, the city shows how strategic planning can help mitigate health risks and protect population well-being.
Residents are encouraged to support these efforts by eliminating standing water around their homes, using mosquito repellents, and staying informed about local health advisories. Every individual action contributes to the broader goal of preventing disease transmission and maintaining community health.












