A Promising New Approach to Alzheimer’s Treatment: Insights from PolyU Research
Scientists at Hong Kong Polytechnic University have uncovered a groundbreaking mechanism that could revolutionize our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases, offering new hope for millions affected by conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Led by Professor Ben Ko Chi-bun, the research centers on tetrandrine, a compound derived from traditional Chinese medicine with remarkable therapeutic potential.
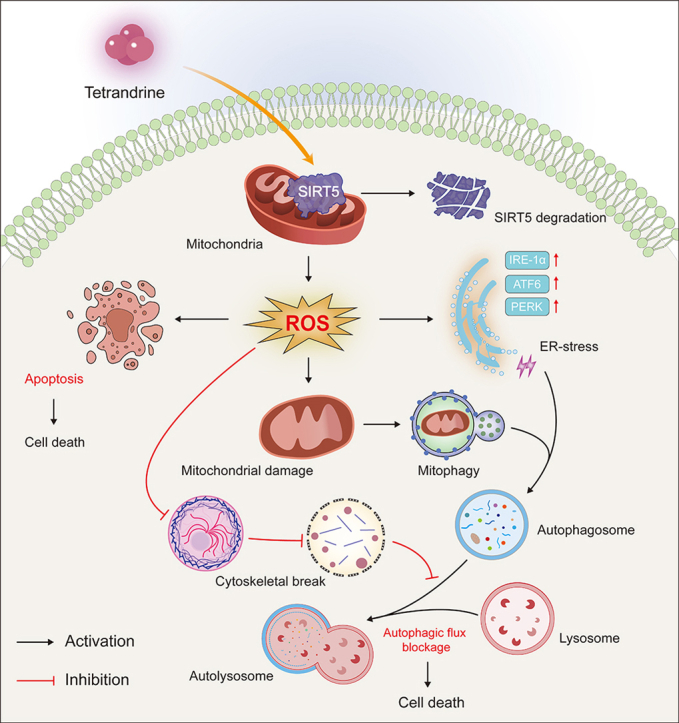
For years, tetrandrine has been recognized for its diverse medicinal properties, including anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects. However, the precise way it works within the human body remained a mystery—until now. Using specialized photoaffinity probes, the research team made a crucial discovery about how tetrandrine interacts with lysosomes, the cellular structures responsible for processing waste and cellular signaling.
The breakthrough lies in tetrandrine’s unique ability to modulate calcium ion release by targeting LIMP-2 proteins on lysosomes. This is significant because calcium signaling plays a critical role in various diseases, particularly neurodegenerative conditions. Unlike previous assumptions that tetrandrine directly affected calcium channels, the research reveals a more nuanced mechanism of calcium regulation.

Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s are characterized by disrupted calcium homeostasis, which contributes to neuronal damage and disease progression. By identifying a new pathway for targeting this cellular process, the PolyU researchers have opened up exciting possibilities for potential treatments. The implications extend beyond Alzheimer’s, with potential applications in cancer treatment and viral infection management.
The team didn’t stop at understanding tetrandrine’s mechanism. They also developed an innovative technology platform that integrates photoaffinity probes with multi-omics analysis—a comprehensive approach that examines biological systems at multiple levels. This cutting-edge platform could serve as a bridge between traditional Chinese medicine and modern scientific research, potentially accelerating the discovery of new therapeutic compounds.
Traditional Chinese medicine has long been used to address various ailments, and this research highlights the untapped potential of natural compounds. By providing a precise method to explore the biological properties of these substances, the PolyU platform could unlock new treatment possibilities across multiple medical fields.
It’s important to note that while the results are promising, the research is still in its early stages. Translating these findings into clinical treatments will require extensive further study to validate the efficacy and safety of tetrandrine-based therapies in humans. Drug development is a complex process that typically takes years of rigorous testing before a new treatment can be brought to market.

Nevertheless, the discovery offers a fresh perspective on addressing some of the most challenging health conditions of our time. Current Alzheimer’s treatments primarily focus on managing symptoms, with no cure currently available. The PolyU research suggests a potential pathway for developing more targeted interventions by focusing on lysosomal calcium signaling.
The broader significance of this research extends beyond a single compound or disease. It demonstrates the power of interdisciplinary approaches that combine traditional medical knowledge with cutting-edge scientific techniques. By carefully examining natural compounds like tetrandrine, researchers can uncover novel mechanisms that could lead to breakthrough treatments for some of the most devastating diseases affecting humanity.
As research continues, the work by Hong Kong Polytechnic University researchers provides a beacon of hope—not just for those suffering from Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, but for the broader field of medical research and drug development.