Introduction:
On July 14, 2025, the Federal Reserve decided to keep interest rates the same, meaning they won’t go up or down for now. This choice comes at a tricky time for the U.S. economy. If we look back to the 1970s, there was a tough period called stagflation, where prices kept rising, but the economy wasn’t growing. Today, some of the same problems, like high prices and slow growth, are showing up again, and this decision by the Federal Reserve is important to understand.
Current Economic Context:
The U.S. economy started shrinking in 2025, which means businesses are making less, and people are spending less. On top of that, tariffs—taxes on goods coming from other countries—are making things harder. These tariffs are pushing up prices for everyday items, which is called inflation. They’re also slowing down the economy because higher prices mean people buy less, and businesses struggle. Tariffs are adding more pressure to an already tough situation by making things more expensive and slowing down growth.

Monetary Policy and Inflation:
After the pandemic, the Federal Reserve printed over $6 trillion to help the economy. But this extra money caused prices to shoot up, with inflation reaching over 9% at one point. To fix this, the Fed reduced the amount of money in the system in 2022 and 2023. However, starting in November 2023, the money supply began to grow again. In April 2025, the M2 money supply, which measures money in banks and cash, jumped by 4.4% compared to last year and 0.7% from the month before. These are the biggest increases since December 2021, and they could mean more inflation is coming.
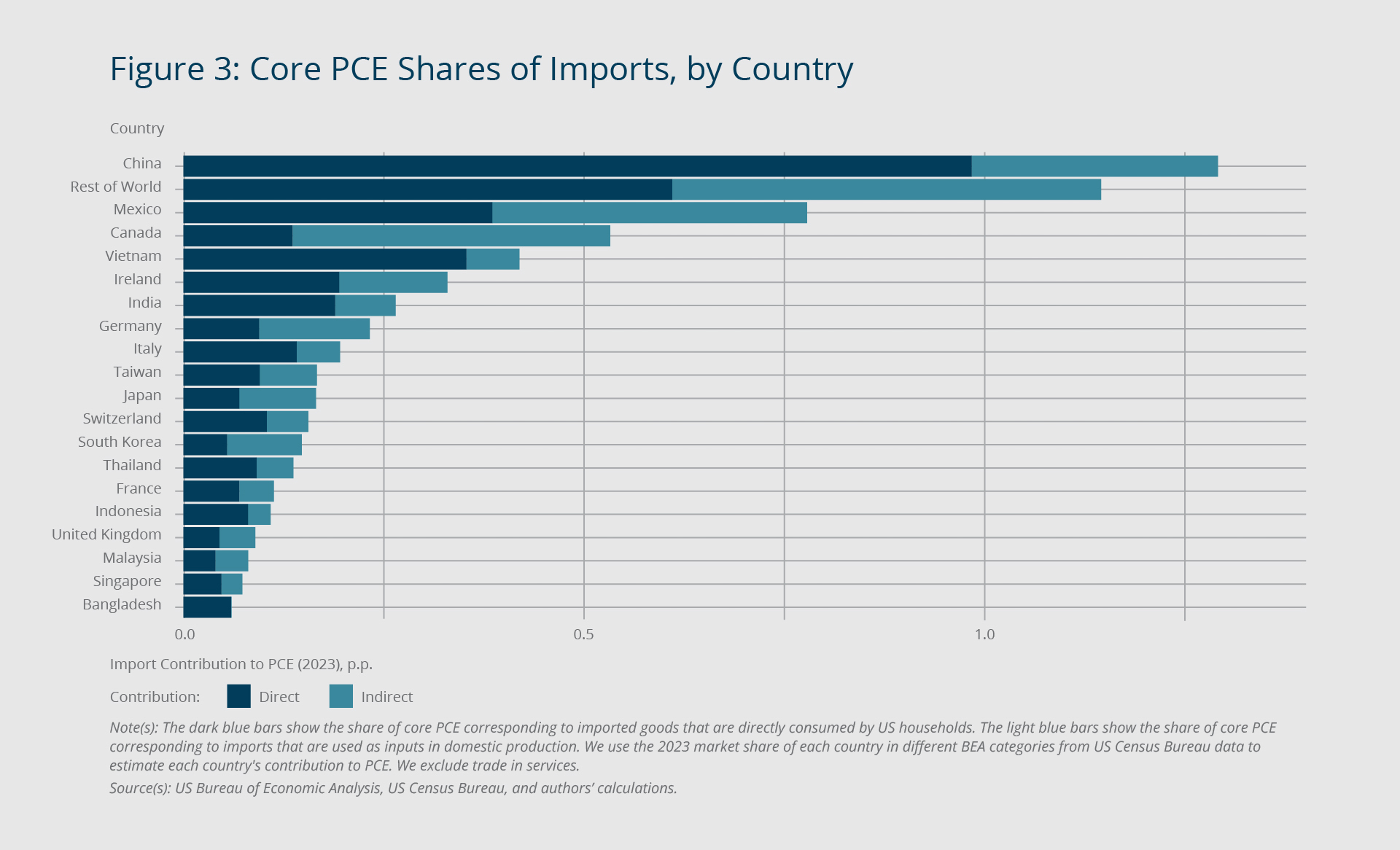
Tariffs and Their Economic Impact:
Tariffs make things more expensive because they raise the cost of goods and materials that come from other countries. For example, if a company has to pay more for steel because of a tariff, they might charge more for their products. This means higher prices for everyone. Tariffs can also mess up supply chains, making it harder for businesses to get what they need. When costs go up, companies often pass them on to customers. This can lead to less spending, which hurts the economy. In the worst case, businesses might even cut jobs if they can’t afford to keep everyone on payroll.
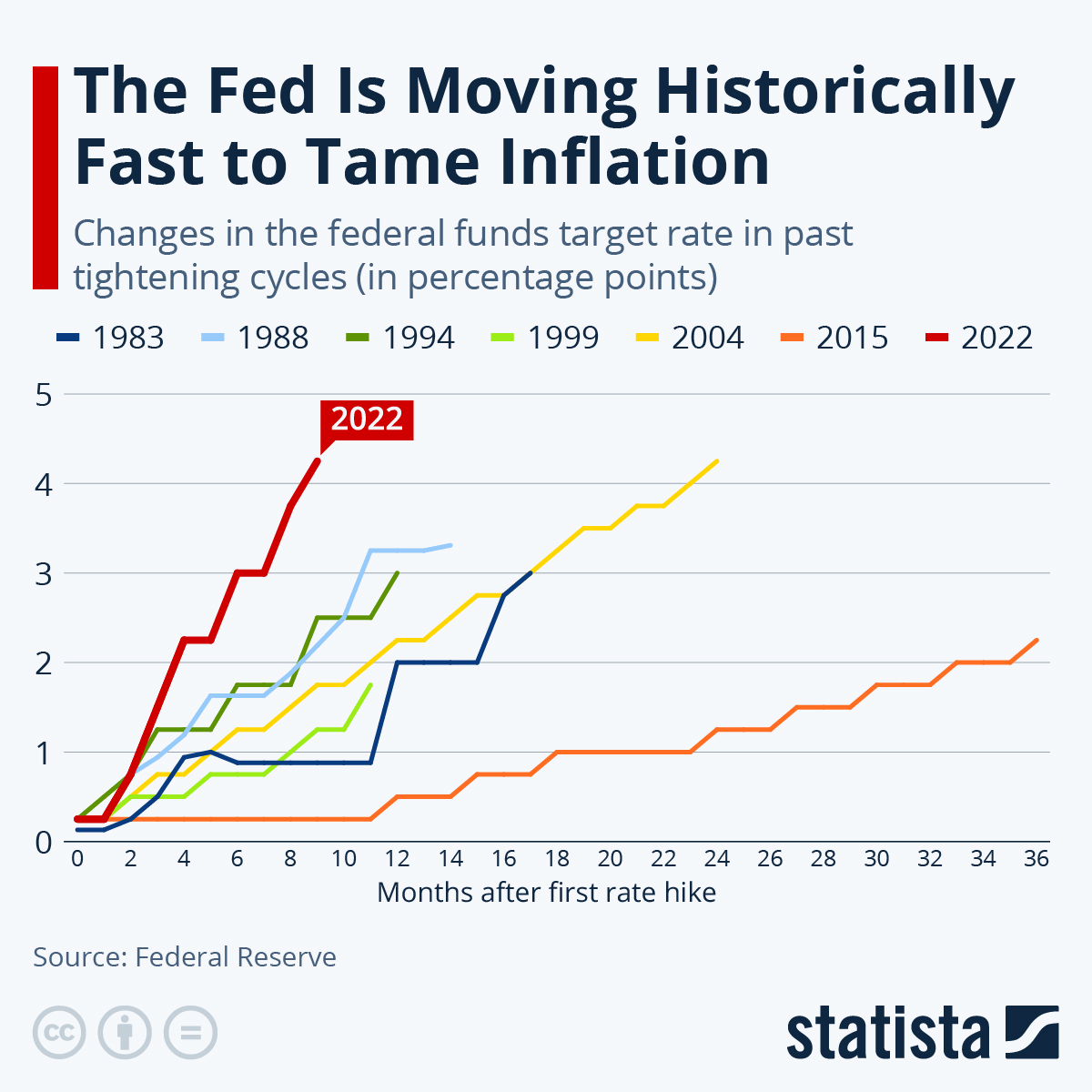
Federal Reserve’s Decision and Its Implications:
The Federal Reserve decided to keep interest rates steady because they’re trying to balance two big goals: keeping prices stable and making sure people have jobs. By not changing rates, they hope to avoid making inflation worse while also not slowing the economy too much. The good side of this decision is that borrowing money won’t get more expensive, which can help businesses and families. But the downside is that inflation might keep going up if there’s too much money in the system. The Fed has to think about both sides—stopping high prices and keeping jobs safe—when they make choices like this.
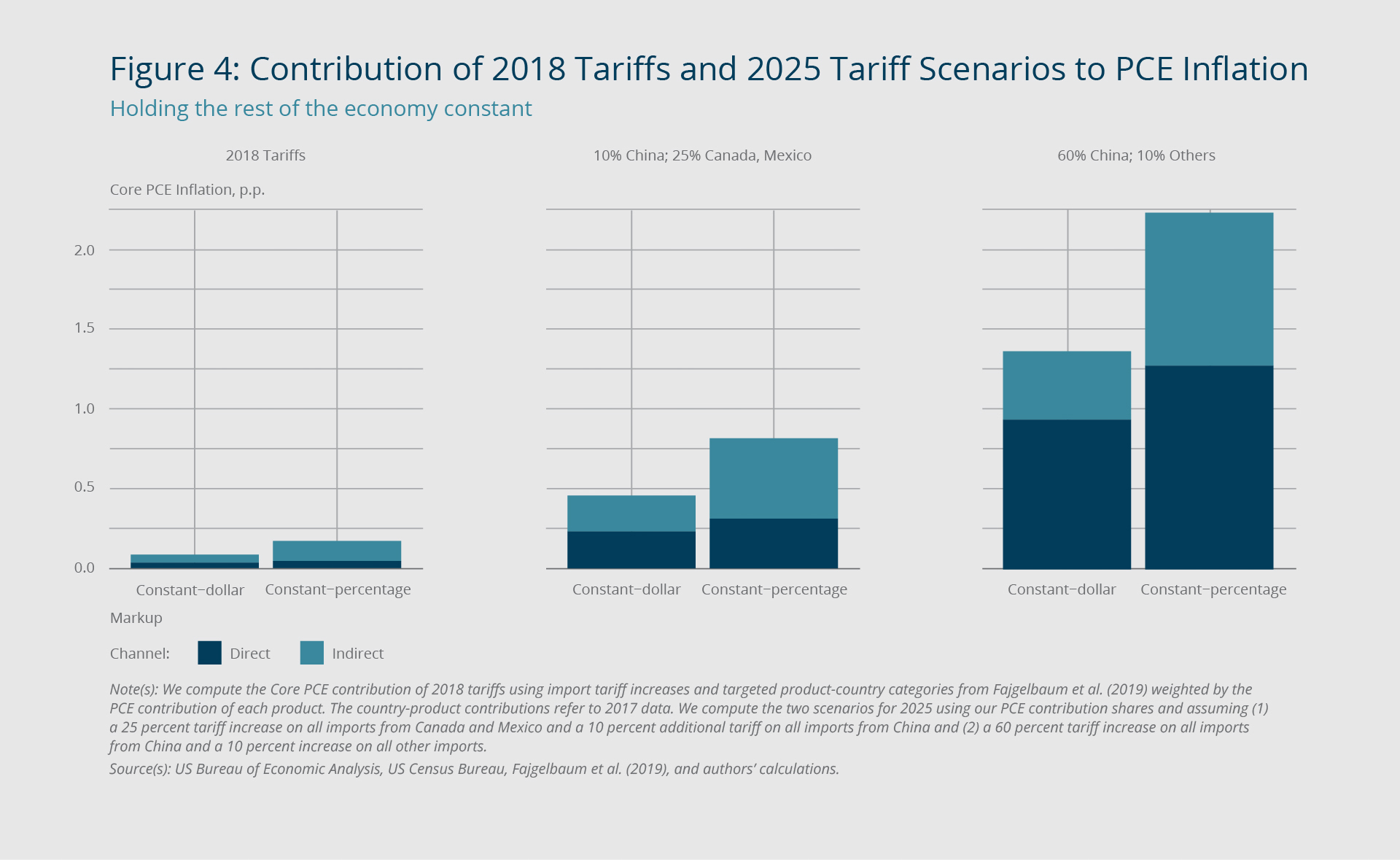
Comparison to the 1970s Stagflation Era:
Back in the 1970s, the U.S. faced stagflation, which meant high inflation and a slow economy at the same time. Prices for things like gas and food went way up, but jobs were hard to find, and businesses weren’t growing. The government and the Federal Reserve tried different things to fix it, like raising interest rates a lot, but it took years to get better. Today, we’re seeing some of the same issues with high prices and a shrinking economy. If tariffs and inflation keep getting worse, we might face similar problems. The big question is whether the Fed’s current plan will work better than the ideas from the 1970s.
Conclusion:
To wrap up, the U.S. economy in 2025 is dealing with a lot of challenges, from tariffs making things more expensive to inflation and slow growth. The Federal Reserve’s choice to keep interest rates the same shows they’re trying to find a balance, but it’s not an easy fix. Tariffs, money supply changes, and inflation all play a part in what happens next. The Fed has a big job to guide the economy through this mess. For now, it’s important for everyone to keep up with the news about the economy and any new policies. Staying informed can help you understand how these changes might affect your life in the coming months.